
Hello, come to consult our products !
يناير . 25, 2025 05:52 Back to list
Factory Supply Agrochemicals Boscalid fungicide 50% WGD WG 98% TC 30% SC
Navigating the Agricultural Landscape Unveiling the Potency and Nuances of Thiamethoxam, Abamectin, and Sulfoxaflor
Sulfoxaflor represents a newer class of insecticides, addressing the challenges posed by pest resistance to older chemical classes. As a sulfoximine, it targets similar receptors as neonicotinoids but offers a novel approach that can be pivotal in resistance management. Sulfoxaflor finds its forte in controlling sap-feeding insects and is valued for its quick action and long-lasting residual effects. The introduction of Sulfoxaflor has ignited debates around environmental safety and regulatory decisions. While it offers an alternative to earlier, more harmful chemicals, it is vital to rigorously assess its ecological footprint. Continued research and adaptation of use guidelines are essential to balance agricultural needs with ecological integrity, emphasizing precision in application to avoid impacts on beneficial arthropods and pollinators. Understanding these components – Thiamethoxam, Abamectin, and Sulfoxaflor – becomes critical in designing effective pest management protocols that reconcile agricultural productivity with environmental stewardship. Farmers, agronomists, and agricultural policymakers bear the responsibility of ensuring these compounds are incorporated into sustainable farming systems. Implementing best practices involves regular monitoring of pest populations and resistance patterns, judicious chemical use complemented by biological and cultural control techniques, and ensuring compliance with region-specific regulatory guidelines. The emphasis on integrated pest management (IPM) cannot be overstressed, highlighting the synergistic potential when combining chemical, biological, and cultural interventions. Emerging digital platforms and precision agriculture tools now empower stakeholders with real-time data and analytics, driving informed decisions on pesticide application and pest control strategies. Such advancements pave the way for reducing the ecological footprints of chemical interventions, ensuring their role remains constructive in meeting global food security demands without undermining environmental sustainability. In the intersection of science, technology, and policy, the judicious use of Thiamethoxam, Abamectin, and Sulfoxaflor highlights the evolving narrative of agriculture – one that is increasingly informed, conscientious, and geared towards harmonious coexistence with nature, underpinned by a commitment to responsibly feed the growing global population.
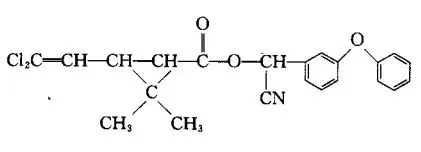

Sulfoxaflor represents a newer class of insecticides, addressing the challenges posed by pest resistance to older chemical classes. As a sulfoximine, it targets similar receptors as neonicotinoids but offers a novel approach that can be pivotal in resistance management. Sulfoxaflor finds its forte in controlling sap-feeding insects and is valued for its quick action and long-lasting residual effects. The introduction of Sulfoxaflor has ignited debates around environmental safety and regulatory decisions. While it offers an alternative to earlier, more harmful chemicals, it is vital to rigorously assess its ecological footprint. Continued research and adaptation of use guidelines are essential to balance agricultural needs with ecological integrity, emphasizing precision in application to avoid impacts on beneficial arthropods and pollinators. Understanding these components – Thiamethoxam, Abamectin, and Sulfoxaflor – becomes critical in designing effective pest management protocols that reconcile agricultural productivity with environmental stewardship. Farmers, agronomists, and agricultural policymakers bear the responsibility of ensuring these compounds are incorporated into sustainable farming systems. Implementing best practices involves regular monitoring of pest populations and resistance patterns, judicious chemical use complemented by biological and cultural control techniques, and ensuring compliance with region-specific regulatory guidelines. The emphasis on integrated pest management (IPM) cannot be overstressed, highlighting the synergistic potential when combining chemical, biological, and cultural interventions. Emerging digital platforms and precision agriculture tools now empower stakeholders with real-time data and analytics, driving informed decisions on pesticide application and pest control strategies. Such advancements pave the way for reducing the ecological footprints of chemical interventions, ensuring their role remains constructive in meeting global food security demands without undermining environmental sustainability. In the intersection of science, technology, and policy, the judicious use of Thiamethoxam, Abamectin, and Sulfoxaflor highlights the evolving narrative of agriculture – one that is increasingly informed, conscientious, and geared towards harmonious coexistence with nature, underpinned by a commitment to responsibly feed the growing global population.
Latest news
-
Hi-Yield Malathion Insecticide | Fast Pest Control Solutions
NewsJul.21,2025
-
Powerful Tolfenpyrad Insecticide for Pest Control Shop Effective
NewsJul.20,2025
-
Herbicide Mesotrione: Advanced Herbicide Solutions for Corn Field Weed Control
NewsJul.12,2025
-
Buy Penoxsulam Herbicide - Selective Weed Control Solution for Lawns & Crops
NewsJul.08,2025
-
Malathion and White Oil Effective Insecticide for Citrus & Ornamentals
NewsJul.08,2025
-
Best Section Fungicide Solutions Effective Carbendazim & Copper Fungicides for Citrus Trees
NewsJul.08,2025
