
Ara . 25, 2024 06:38 Back to list
buy abamectin ld50
Understanding Abamectin and Its Toxicity The LD50 Metric
Abamectin is an important chemical used primarily as an insecticide and acaricide in agricultural practices. It is derived from the fermentation of the soil bacterium *Streptomyces avermitilis*. With its versatility in combating a wide array of pests, from mites to insects, abamectin has become a staple in integrated pest management strategies. However, understanding its safety profile, particularly its toxicity levels, is crucial for both consumers and agricultural professionals. A key metric in this assessment is the LD50 value.
What is LD50?
LD50, or lethal dose 50, refers to the quantity of a substance that is sufficient to kill 50% of a test population, usually laboratory animals such as rats or mice, when administered via a specific route (oral, dermal, or inhalation). The LD50 is measured in milligrams of substance per kilogram of body weight (mg/kg). This figure is essential for understanding the acute toxicity of a substance—how it poses a risk to humans, animals, and the environment.
In the case of abamectin, its oral LD50 is reported to be around 5 mg/kg in rats, which categorizes it as moderately toxic. This means that while it poses a significant risk if ingested or if there is significant exposure, it is less toxic compared to highly hazardous materials with significantly lower LD50 values.
Mechanism of Action
Abamectin operates by affecting the neurotransmission in pests. It binds to glutamate-gated chloride channels in the nervous system, leading to increased permeability of cell membranes to chloride ions. This disruption inhibits nerve impulse transmission, causing paralysis and death in the targeted pests. While this mechanism effectively controls pest populations, it also raises concerns regarding its potential impacts on non-target organisms, including humans and beneficial insects.
Human Health Risks
buy abamectin ld50
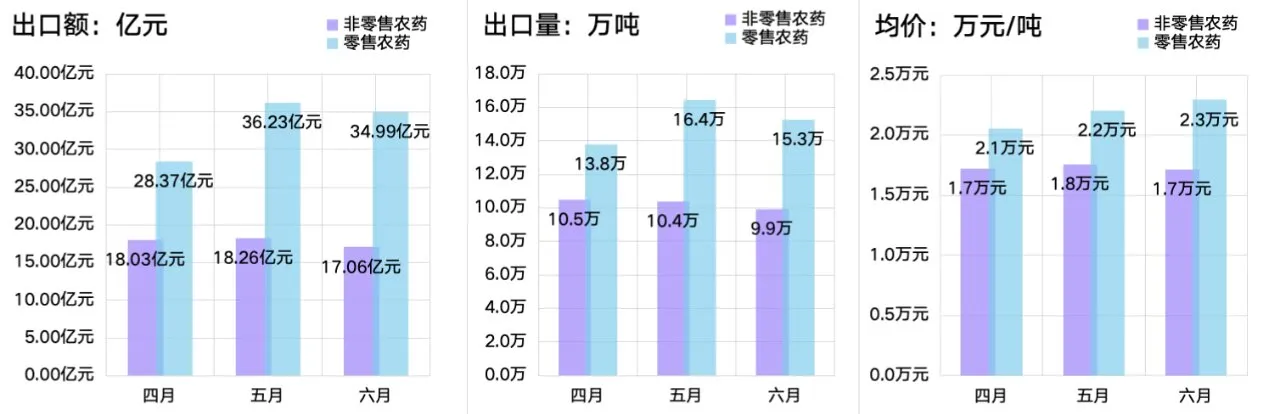
For humans, the primary risk associated with abamectin exposure comes from its use in agricultural settings. Farmers and agricultural workers can be exposed through inhalation, skin contact, or ingestion if proper protective measures are not observed. Symptoms of acute exposure can include dizziness, nausea, and, in severe cases, respiratory distress. Furthermore, the toxicological profile of abamectin raises concerns about its potential effects on sensitive populations, such as pregnant women and those with compromised immune systems.
Given its moderate toxicity, regulatory agencies have established guidelines regarding its application. In the United States, for instance, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets strict limits on the maximum residue level of abamectin on food crops to mitigate health risks. Consumers should also be aware of these regulations when purchasing produce, as adhering to these guidelines can reduce health risks associated with pesticide exposure.
Environmental Impact
Beyond human health, the use of abamectin raises concerns about its environmental impact. Its mode of action suggests that it is not only harmful to target pests but may also affect non-target organisms, including beneficial arthropods and aquatic life. There have been instances of abamectin runoff leading to toxic conditions in waterways, where it affects fish and amphibians.
The persistence of abamectin in the environment varies depending on factors such as soil type and microbial activity. Nevertheless, farmers are encouraged to adopt best management practices that minimize its environmental impact. This includes using it judiciously, following label instructions carefully, and incorporating integrated pest management techniques to reduce reliance on chemical controls.
Conclusion
In summary, abamectin represents a crucial tool in modern agriculture for pest control. However, understanding its toxicity, especially as indicated by the LD50 value, is essential for safe usage. With a reported oral LD50 of approximately 5 mg/kg in rats, it demands cautious handling and application among agricultural workers and consumers alike. By observing safety regulations and best practices, the benefits of abamectin can be harnessed while minimizing potential health risks and environmental impacts. As agriculture continues to evolve, the responsible use of such chemicals will be critical in ensuring both effective pest management and the safety of human and ecological health.
-
Dicamba Herbicide for Creeping Charlie – Effective & Selective Weed Control Solution
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Premium Penthiopyrad Fungicide for Effective Crop Protection Compare with Carbendazim & Copper Fungicides
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Top Products Containing Bifenthrin Effective Insecticide Solutions
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Powerful Lambda Cyhalothrin & Emamectin Benzoate Insecticide
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Emamectin Benzoate 5% Wholesale Supplier - Premium Quality
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Indoxacarb PubChem Key Pesticide Properties & Benefits
NewsJun.09,2025
