
اکتوبر . 09, 2024 12:23 Back to list
Recommended Dosages for Acetamiprid Insecticide in China for Effective Pest Control
Understanding Acetamiprid Insecticide Dosage in China
Acetamiprid, a neonicotinoid insecticide, has gained significant attention in agricultural practices across China due to its effectiveness in controlling a wide range of pests. As a synthetic derivative of nicotine, acetamiprid targets the nervous system of insects, providing rapid knockdown and prolonged efficacy. Given its importance in the agricultural sector, understanding the appropriate dosage of acetamiprid for various applications is crucial for maximizing pest control while minimizing potential negative impacts on beneficial organisms and the environment.
Understanding Acetamiprid Insecticide Dosage in China
It is essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions and local agricultural guidelines when applying acetamiprid. Typically, the recommended concentration for foliar applications is between 0.02% and 0.1%, depending on the specific crop and pest. Thorough coverage is vital, as acetamiprid is most effective when it can penetrate the protective layers of the plants and reach the pests directly.
china acetamiprid insecticide dosage
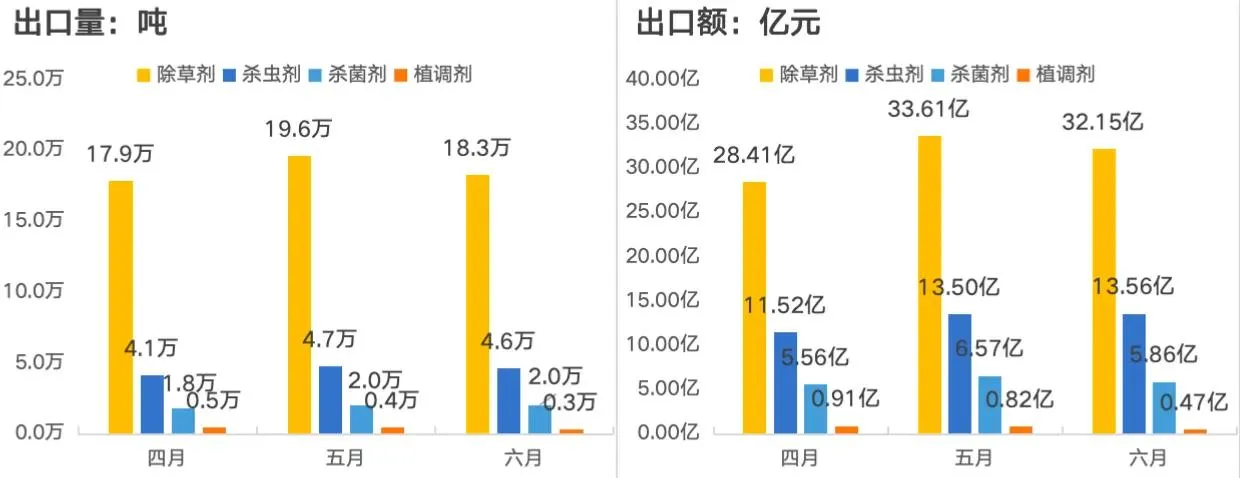
Furthermore, timing plays a critical role in the efficacy of acetamiprid. Applying the insecticide during the early stages of pest infestation can lead to better control and reduce the overall amount needed. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies are often recommended alongside chemical applications to enhance efficacy and sustainability. By combining acetamiprid with cultural practices, biological controls, and other pest management strategies, farmers can achieve better outcomes while reducing reliance on chemical solutions alone.
Despite its advantages, the use of acetamiprid is not without controversy. Concerns regarding its impact on non-target species, including pollinators like bees, have led to increased scrutiny and regulation. Therefore, it is vital for farmers to consider alternative pest management strategies and to use acetamiprid judiciously to mitigate potential harm to beneficial organisms. Applying the insecticide during times of day when pollinator activity is low, such as early morning or late evening, can help reduce exposure risks.
In addition, monitoring pest populations and scouting fields regularly are essential practices in determining the need for insecticide applications. This approach can prevent unnecessary treatments and help manage resistance development among pest populations. Farmers are encouraged to stay informed about any updates in regulations and recommendations regarding acetamiprid usage.
In conclusion, acetamiprid is a valuable tool for pest management in China's agricultural landscape. By understanding proper dosages, application timing, and integrating other pest management strategies, farmers can utilize this insecticide effectively while promoting environmental sustainability. Continued research and communication within the agricultural community will be vital in optimizing the use of acetamiprid and ensuring its role in sustainable agriculture for the future.
-
Herbicide Mesotrione: Advanced Herbicide Solutions for Corn Field Weed Control
NewsJul.12,2025
-
Buy Penoxsulam Herbicide - Selective Weed Control Solution for Lawns & Crops
NewsJul.08,2025
-
Malathion and White Oil Effective Insecticide for Citrus & Ornamentals
NewsJul.08,2025
-
Best Section Fungicide Solutions Effective Carbendazim & Copper Fungicides for Citrus Trees
NewsJul.08,2025
-
Types of Herbicides Explained Discover 5 Types of Selective Herbicides for Effective Weed Control
NewsJul.07,2025
-
Buy Bifen Chemical – Safe Termiticide for Dogs & Effective Pest Control Solutions
NewsJul.07,2025
